Python製の三目並べ
はじめに
Pythonで作成した「三目並べ」です。
ソースコード
python/tic-tac-toe.py at master · ki-hi-ro/python
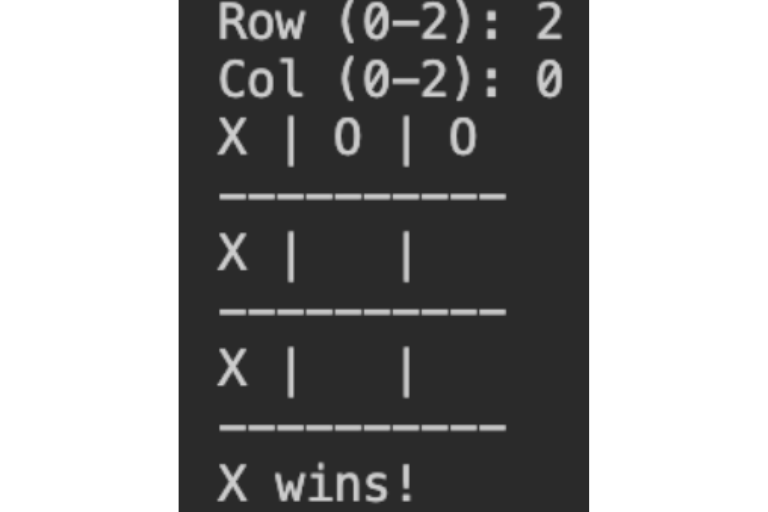
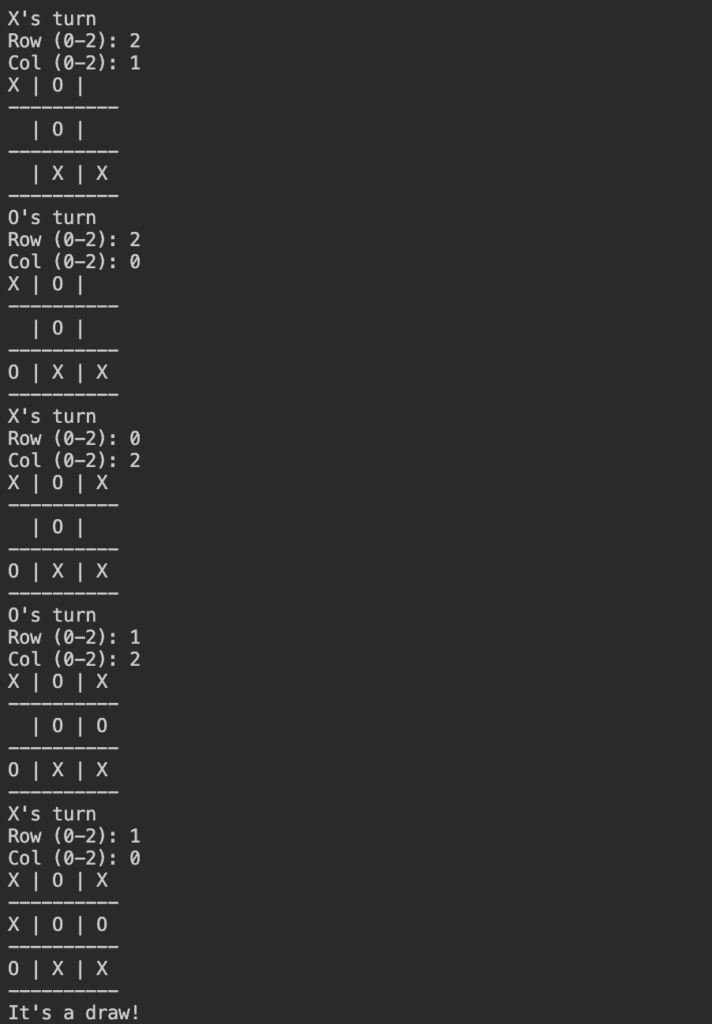
プレイヤーXが勝つようにプレイ
実行すると空の盤面が表示され、プレイヤーXのターンが始まります。行と列の数字を入力して、(0, 0)の位置にXが入力されました。プレイヤーOにターンが変わります。X→O→X→O→Xとゲームが進んでいき、0行目がすべて揃ったので、Xの勝ちです。

引き分けになるようにプレイ

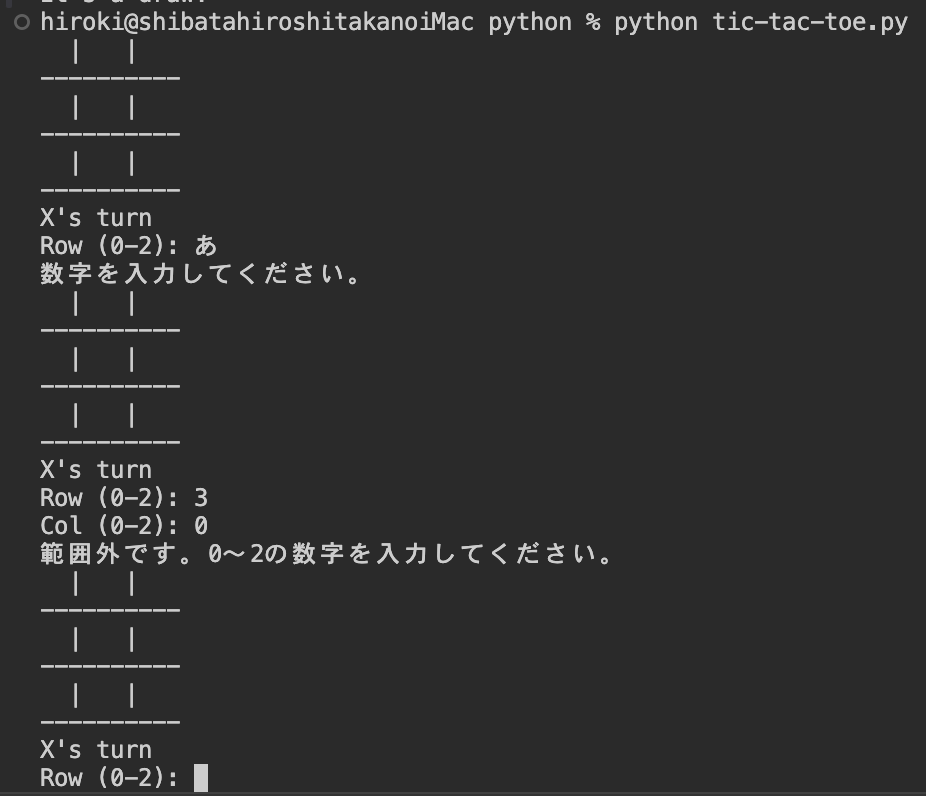
ユーザー入力数字のバリデーション
数字以外が入力されたら、「数字を入力してください。」と表示されます。0 ~ 2の範囲外の数字が入力されたら、「範囲外です。0 ~ 2の数字を入力してください」と表示されます。
メイン処理
main関数を起動しています。
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()main関数はこちらです。まずは、空の盤面のリストを定義しています。次に、プレイヤークラスのインスタンスとして、xとoの二つを作成して、現在のプレイヤーをxに設定しています。while文を使用して、ループ処理を行っています。display_boad関数でボードを表示して、現在のプレイヤーを表示しています。inputでユーザからの入力を受け付けています。数字以外が入力された場合の例外処理を行っています。範囲外の場合も対応しています。make_move関数の処理、check_winner関数の処理、is_full関数の処理を行っています。最後に、現在のプレイヤーの切り替えを行っています。
def main():
board = [[" " for _ in range(3)] for _ in range(3)] # 空の盤面
player_x = Player("X")
player_o = Player("O")
current_player = player_x
while True:
display_board(board)
print(f"{current_player.symbol}'s turn")
try:
row = int(input("Row (0-2): "))
col = int(input("Col (0-2): "))
except ValueError:
print("数字を入力してください。")
continue
if not (0 <= row <= 2 and 0 <= col <= 2):
print("範囲外です。0〜2の数字を入力してください。")
continue
if not make_move(board, row, col, current_player.symbol):
print("そのマスはすでに埋まっています。")
continue
if check_winner(board, current_player.symbol):
display_board(board)
print(f"{current_player.symbol} wins!")
break
if is_full(board):
display_board(board)
print("It's a draw!")
break
current_player = player_o if current_player == player_x else player_x空の盤面のリスト
board
[[' ', ' ', ' '], [' ', ' ', ' '], [' ', ' ', ' ']]プレイヤーの初期設定
player_x = Player("X")
player_o = Player("O")
current_player = player_x盤面と現在のプレイヤーの表示
display_board(board)
print(f"{current_player.symbol}'s turn")ユーザから数値の入力を受け付ける
try:
row = int(input("Row (0-2): "))
col = int(input("Col (0-2): "))
except ValueError:
print("数字を入力してください。")
continue
if not (0 <= row <= 2 and 0 <= col <= 2):
print("範囲外です。0〜2の数字を入力してください。")
continuemake_move関数の処理
if not make_move(board, row, col, current_player.symbol):
print("そのマスはすでに埋まっています。")
continuecheck_winner関数の処理
if check_winner(board, current_player.symbol):
display_board(board)
print(f"{current_player.symbol} wins!")
breakis_full関数の処理
if is_full(board):
display_board(board)
print("It's a draw!")
break現在のプレイヤーの切り替え
current_player = player_o if current_player == player_x else player_xプレイヤーを表すクラス
定義はこちらです。コンストラクタで、インスタンス変数のself.symbolを設定できます。
# プレイヤーを表すクラス
class Player:
def __init__(self, symbol):
self.symbol = symbol # 'X' または 'O'メイン処理で、xとoの二つのインスタンスを生成しています。
player_x = Player("X")
player_o = Player("O")盤面を表示する関数
定義はこちらです。boadから要素を取り出して、「 | 」で連結したものを表示して、-を1回繰り返したものを表示します。
# 盤面を表示する関数
def display_board(board):
for row in board:
print(" | ".join(row))
print("-" * 10)メイン処理では、3箇所で使用しています。
# メイン処理
def main():
board = [[" " for _ in range(3)] for _ in range(3)] # 空の盤面
player_x = Player("X")
player_o = Player("O")
current_player = player_x
while True:
display_board(board)
print(f"{current_player.symbol}'s turn")
try:
row = int(input("Row (0-2): "))
col = int(input("Col (0-2): "))
except ValueError:
print("数字を入力してください。")
continue
if not (0 <= row <= 2 and 0 <= col <= 2):
print("範囲外です。0〜2の数字を入力してください。")
continue
if not make_move(board, row, col, current_player.symbol):
print("そのマスはすでに埋まっています。")
continue
if check_winner(board, current_player.symbol):
display_board(board)
print(f"{current_player.symbol} wins!")
break
if is_full(board):
display_board(board)
print("It's a draw!")
break
current_player = player_o if current_player == player_x else player_x一番最初の盤面
最初は以下のように表示されます。まっさらな状態です。
2回目以降の盤面
2回目以降は以下のようにマークがついています。
勝者がいた場合の盤面
1列目が全部Xで埋まっている場合です。

引き分けの場合の盤面
全てのマスが埋まっている場合です。

マスにマークを置く関数
# マスにマークを置く関数
def make_move(board, row, col, symbol):
if board[row][col] == " ":
board[row][col] = symbol
return True
return False勝者を判定する関数
# 勝者を判定する関数
def check_winner(board, symbol):
win_conditions = [
# 横
[(0,0), (0,1), (0,2)],
[(1,0), (1,1), (1,2)],
[(2,0), (2,1), (2,2)],
# 縦
[(0,0), (1,0), (2,0)],
[(0,1), (1,1), (2,1)],
[(0,2), (1,2), (2,2)],
# 斜め
[(0,0), (1,1), (2,2)],
[(0,2), (1,1), (2,0)]
]
for condition in win_conditions:
if all(board[r][c] == symbol for r, c in condition):
return True
return False引き分けを判定する関数
# 引き分け(満杯)を判定
def is_full(board):
return all(cell != " " for row in board for cell in row)
コメントを残す