2025.07.26(更新日: 2025.10.04)
幅優先探索で最短経路を求める
はじめに
前回は、プレーンな幅優先探索を行なった。
今回やりたいのは、最短経路探索。
ブラックボックスをいかに使いこなすか
人体の仕組みをはじめとして、ブラックボックスになっていることは多い。
その中身を知ろうとすると、膨大な時間がかかる。
プログラミングにおける関数も中身を知らなくても、入力(引数)と出力(戻り値)だけ意識すれば、うまく組み合わせることで、プログラムを作成していける。
最短経路検索の関数
from collections import deque
def bfs_shortest_path(graph, start, goal):
queue = deque([[start]]) # キューに「経路のリスト」を入れる
visited = set() # 訪問済みノード
while queue:
path = queue.popleft() # 現在の経路
node = path[-1] # 現在のノード
if node == goal:
return path # 最短経路が見つかった!
if node not in visited:
visited.add(node)
for neighbor in graph[node]:
new_path = path + [neighbor] # 新しい経路を作成
queue.append(new_path)
return None # 経路が見つからなかった場合
# 使用例
graph = {
'A': ['B', 'C'],
'B': ['D', 'E'],
'C': ['F'],
'D': [],
'E': ['F'],
'F': []
}
start_node = 'A'
goal_node = 'F'
shortest_path = bfs_shortest_path(graph, start_node, goal_node)
print("最短経路:", shortest_path)実行結果
最短経路: ['A', 'C', 'F']グラフのイメージ
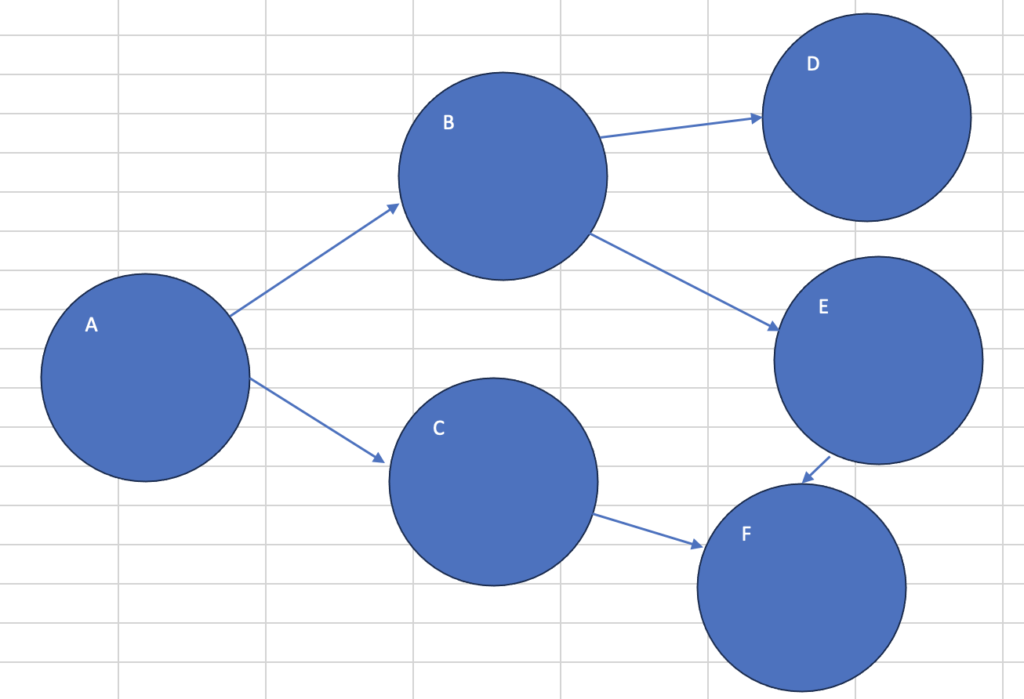
Aがスタート、Fがゴール
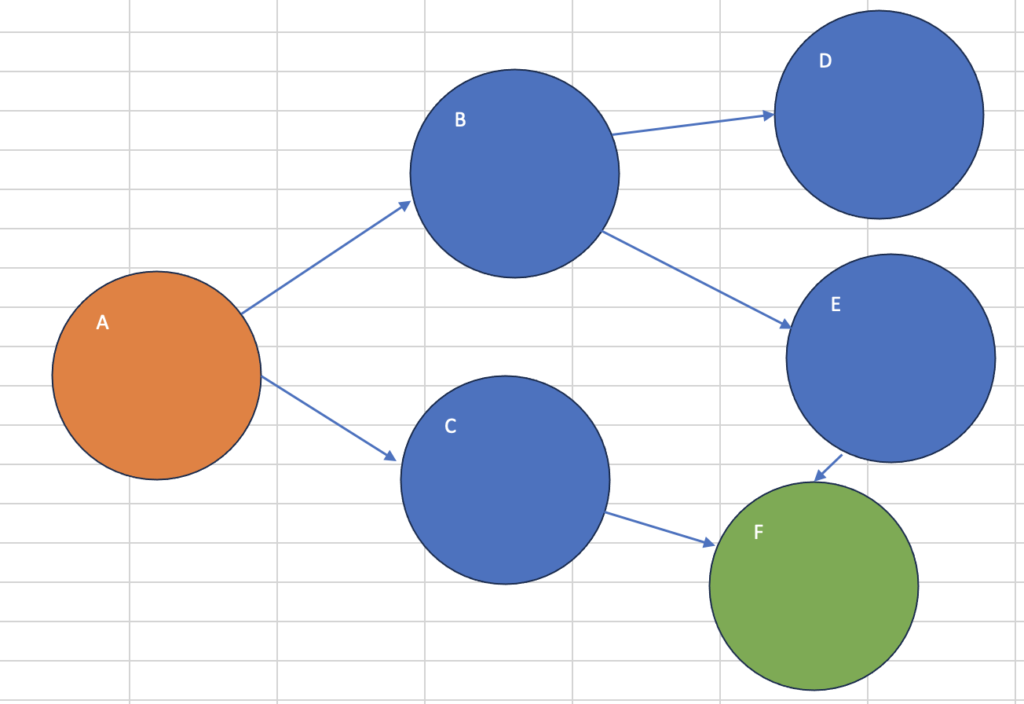
最短経路は、A→C→F。
Aがスタート、Eがゴール
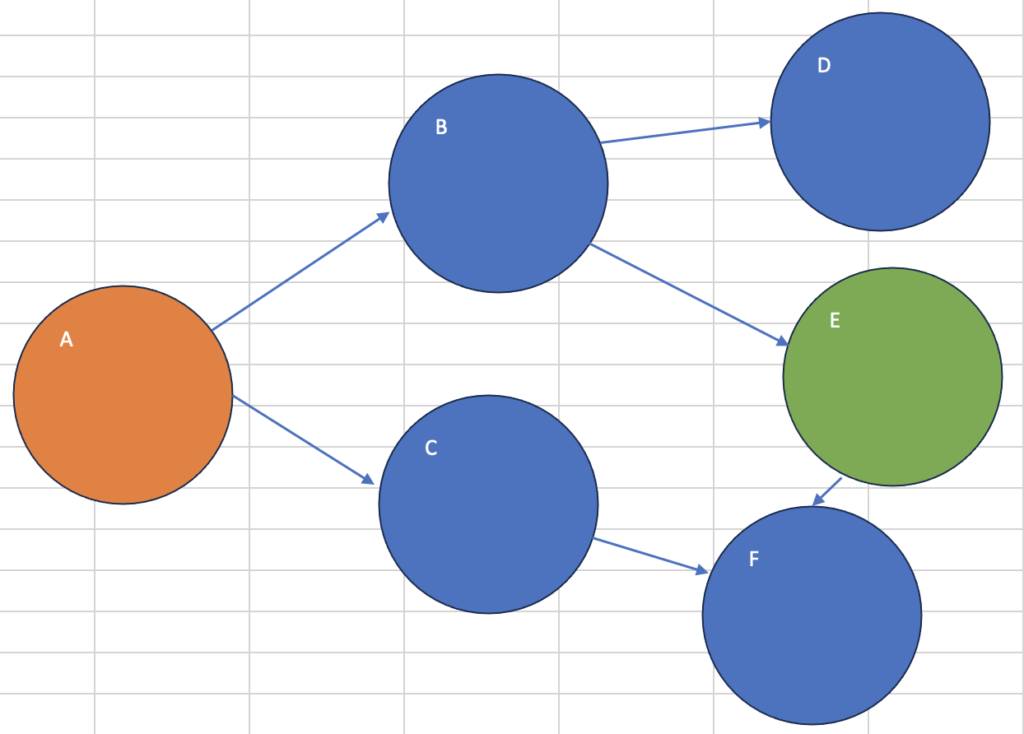
start_node = 'A'
goal_node = 'E'
shortest_path = bfs_shortest_path(graph, start_node, goal_node)
print("最短経路:", shortest_path)最短経路: ['A', 'B', 'E']Cがスタート、Bがゴール(異常系)
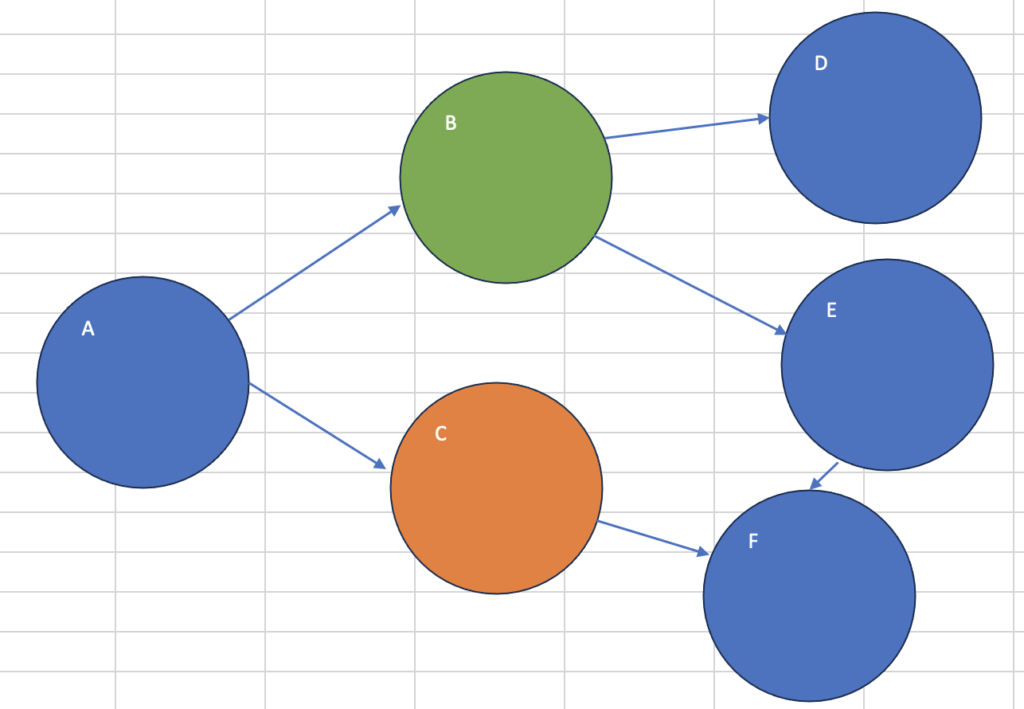
start_node = 'C'
goal_node = 'B'
shortest_path = bfs_shortest_path(graph, start_node, goal_node)
print("最短経路:", shortest_path)最短経路: None
コメントを残す